Applications of Protection Relays in Real-World Electrical Systems

Applications of Protection Relays in Real-World Electrical Systems
In today’s world, every industry depends on reliable and safe power. Even a small electrical fault can cause huge financial losses, downtime, or life-threatening hazards. Protection relays act as the “silent guardians” of power systems – continuously monitoring current, voltage, frequency, and power factor, and instantly tripping the faulty section to save the equipment.
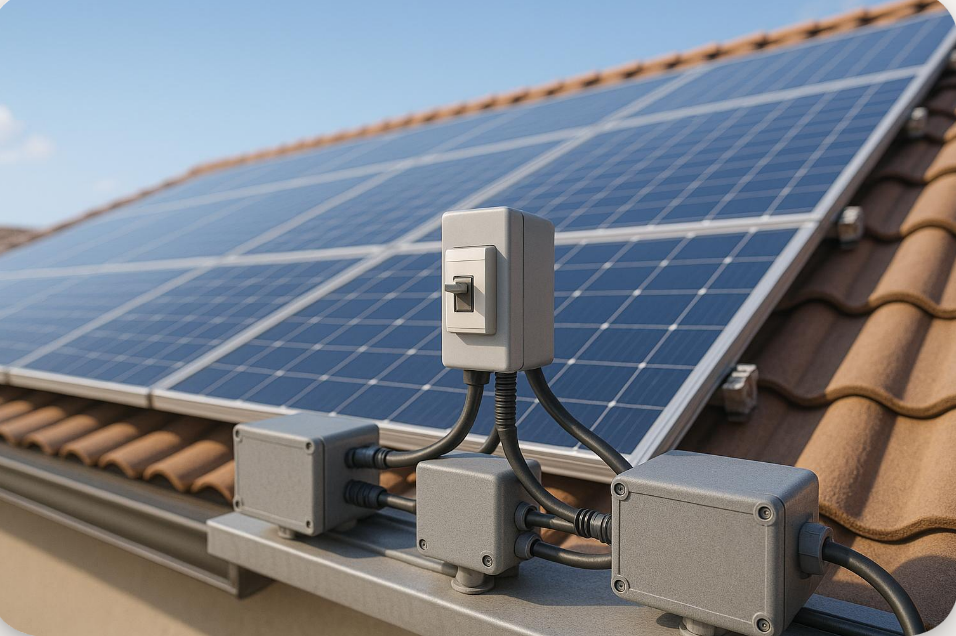
1. How Protection Relays Are Used in Solar Industry
Solar plants generate renewable energy but are directly connected to the utility grid. Any fault can affect both the plant and the grid. Protection relays play a critical role here:
Overvoltage / Undervoltage Protection: Prevents damage to solar inverters and panels during sudden grid fluctuations.
Frequency Protection: Disconnects the solar plant when grid frequency goes beyond safe limits (e.g., >51 Hz or <47 Hz in India).
Anti-Islanding Protection: When the grid supply fails, the relay ensures the solar plant is isolated to avoid “back-feeding” which can be dangerous for utility workers.
Harmonic Monitoring: Multifunction relays detect high harmonics generated by inverters and protect sensitive loads.
- Without protection relays, solar farms could destabilize the grid and face massive equipment damage.

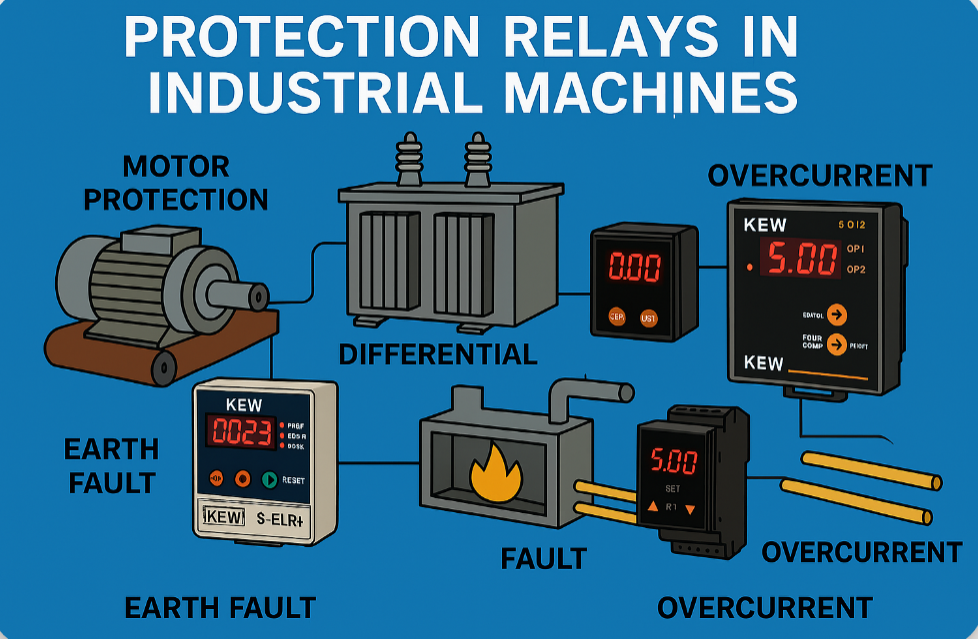
2. How Protection Relays Are Used in Industrial Machines
Industries rely on machines like motors, compressors, pumps, and furnaces that consume huge amounts of electricity. Faults in such systems can stop entire production lines. Relays ensure safe operation:
Motor Protection Relays: Detect overloads, single-phasing, and locked rotor conditions, preventing motor burnouts.
Differential Relays: Protect large industrial transformers by sensing internal faults between windings.
Earth Fault Relays: Trip the circuit if current leaks to earth, reducing the risk of fire and shock hazards.
Overcurrent Relays: Ensure cables and busbars do not overheat due to excess current.
- Example: In a steel plant, if a furnace transformer develops an internal fault, a differential relay isolates it instantly, preventing fire and saving crores in downtime.
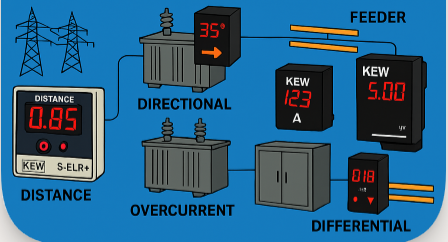
3. How Protection Relays Are Used in Utilities / Substation Panels
Utilities and substations are the heart of power distribution. A single failure here can cause city-wide blackouts. Relays are the first line of defense:
Distance Relays: Protect long transmission lines from line-to-line or line-to-ground faults.
Directional Relays: Ensure faults are cleared only in the fault direction (avoiding wrong trips).
Overcurrent & Earth Fault Relays: Protect busbars, cables, and distribution feeders.
Differential Relays for Transformers: Detect faults inside substation transformers and trip before damage spreads.
- Example: During a storm, if a tree branch touches a transmission line, the distance relay detects fault location and trips only that section, keeping the rest of the grid stable.
4. How Protection Relays Are Used in Generators & DG Sets
Generators and DG sets are expensive assets that require reliable protection to avoid breakdowns:
Reverse Power Relay: Prevents a generator from absorbing power (instead of supplying) during synchronization failures.
Under/Over Frequency Relays: Ensure the generator runs within safe frequency range.
Voltage Protection Relays: Prevent overvoltage or undervoltage conditions that can damage alternators.
Load Monitoring & Run Hour Relays: Track usage for maintenance schedules.
- Example: In hospitals, DG sets provide emergency backup. Relays ensure safe operation during sudden load changes, preventing life-support machines from shutting down.
luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

5. How Protection Relays Are Used in Building Management Systems (BMS)
Modern buildings rely on automation and uninterrupted power. Relays are integrated with BMS systems for safety:
Elevators: Protected from short circuits and overloads.
HVAC Systems: Relays trip faulty air handling units, preventing fire risks.
Data Centers: Multifunction relays measure PF, kWh, kVAh and detect faults, ensuring 24×7 uptime.
Sub-Metering: Relays help monitor each tenant’s energy usage.
- Example: In IT parks, relays prevent server rooms from sudden outages by isolating faulty feeders, keeping data centers online.

6. How Protection Relays Are Used in Wind Energy Systems
Wind turbines face highly fluctuating electrical and mechanical stresses. Relays protect against these challenges:
Over-Speed & Frequency Relays: Trip turbines during overspeed or unstable frequency.
Generator Protection Relays: Safeguard alternators from short circuits.
Grid Synchronization Relays: Maintain smooth connection between wind farm and grid.
- Example: In coastal wind farms, sudden gusts can push turbines into overspeed. Relays trip them safely, avoiding catastrophic damage.

7. How Protection Relays Are Used in Railways & Metro Systems
Railways and metros depend on continuous power for traction, signaling, and passenger comfort. Relays ensure:
Traction Substation Protection: Overcurrent & earth fault relays protect transformers.
Overhead Line Protection: Distance relays clear faults in long traction lines.
Signaling Circuits: Sensitive relays prevent false triggering and accidents.
- Example: In metro systems, if a short circuit occurs in one feeder, relays isolate that section while trains continue safely on other routes.

8. How Protection Relays Are Used in Industrial Automation & Smart Grids
The future of electricity is smart grids and automation. Relays are now intelligent devices:
Communication Relays: Support Modbus/RS-485 for SCADA monitoring.
Event Logging & Alarms: Store fault history for predictive maintenance.
IoT-enabled Relays: Remote monitoring from mobile apps or control centers.
- Example: In smart factories, relays send real-time fault alerts to engineers, preventing downtime before it happens.

Final Thoughts
Protection relays are no longer just trip devices – they are multi-functional guardians of modern electrical systems. From solar farms to hospitals, wind turbines to smart grids, relays ensure:
- Equipment safety
- Human safety
- Power reliability
- Reduced downtime
Wherever electricity flows, protection relays silently safeguard the system.



